Thesis: Analysis of the Impacts of Urban Form on Primary Students’ Travel Patterns and Physical Activity (The Case Study of Shiraz)
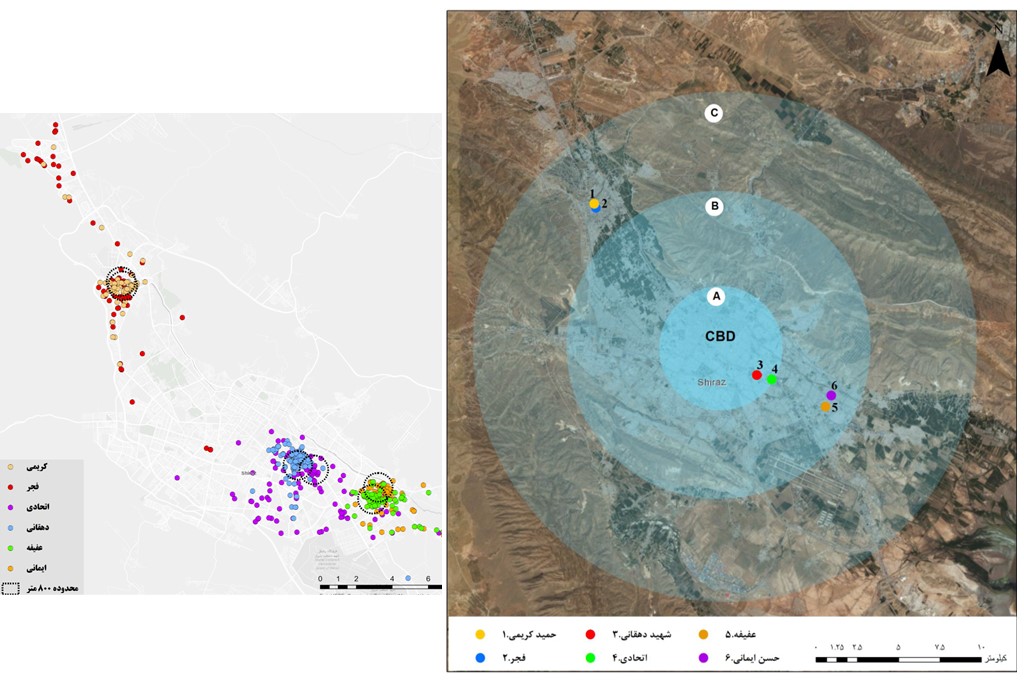

In recent decades, overweight and obesity have been increased in children due to their sedentary lifestyle and increased use of motor vehicles. On the other hand, previous studies have shown that the urban form is directly associated with active travels and physical activities of the children by facilitating commuting, guaranteeing safety for them, and improving access to the schools. Therefore, evaluating the relationship of urban form with active travel is essential for encouraging the children to use active travels when going to school or in their leisure time. Accordingly, the present study makes an effort to investigate the effects of elements of urban form on the travel patterns and physical activities of the elementary students. The information about individual, interpersonal, and economic-social characteristics of 558 students and their families in six state elementary schools of Shiraz was collected. The urban form information, including land use, transport infrastructure, density, housing type, and layout, has been extracted, and the effective factors in the students’ travel have been analyzed using the binary logit regression model. The results showed that the factors student age and sex, number of students in household, Number of driving license holders in household, the commuting pattern of the mother, and the parents’ attitude toward the streets leading to the school had a particular relationship with the active travels of the children. Moreover, among the elements of urban form, the street connectivity, portion of service use around the house, distance from school, and walkability catchment within an 800-m radius of the school had a clear relationship with the travel pattern of the student.
Descriptions and Authors
Masoud Javadpoor
September 2019
